Surety Bonds
The IRDAI has released guidelines to promote and regulate a justifiable and healthy development of the surety insurance business in India. This came after Union Finance Minister Nirmal Sitharaman gave the green light to surety bonds as an alternative to bank guarantees...
The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has released guidelines to promote and regulate a justifiable and healthy development of the surety insurance business in India. This came after Union Finance Minister Nirmal Sitharaman gave the green light to surety bonds as an alternative to bank guarantees for government contracts while presenting the Union Budget 2022-23. Beginning in April 2022, the guidelines will be implemented.
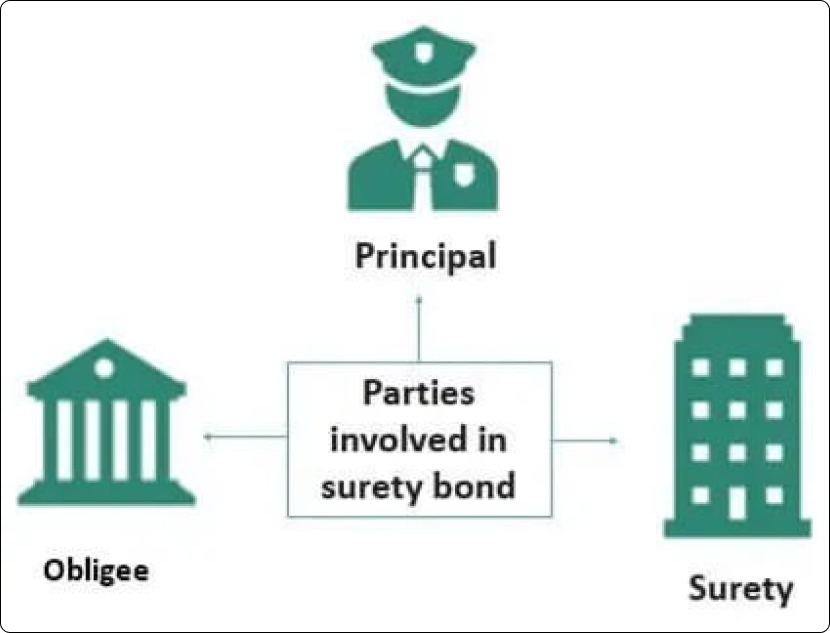
Business contracts must be executed to deliver the agreed/specified outcome or rated performance. The Obligee (customer) often perceives that monetizing the commitments of the Principal (supplier/contractor) enables self-governance and ensures compliance with contractual terms. Therefore, the Principal is asked to provide a bank guarantee for which they are required to provide 10% of the contract's guarantee amount as margin money through a fixed deposit and other collateral for the balance guarantee amount. It indicates that the bank guarantee implies an additional cost of 5% to 15% for the Principal.
For ease of doing business, GOI announced to allow surety bonds by contractors for use as performance guarantees in government procurements. With surety bonds, micro and small enterprises, which did not previously have access to formal financial services, will be able to get guarantees.
Further, GOI has mandated PSUs and government departments to procure at least 30 per cent of their annual purchases from micro and small enterprises.
Sureties are a new product in India. A surety is a tripartite agreement between the Principal (supplier/contractor), the Obligee (customer) and the Surety provider (insurance company).
Get the best All Risk quote
You name any insurable interest- we can get it insured for you
Types of Surety Contracts
Insurance companies can offer the following six types of sureties.
-
Advance Payment Bond: It assures that if the contractor cannot fulfil the contract, the Surety provider will pay the outstanding balance of the advance payment.
-
Bid Bond: The bidder undertakes the obligation to provide a prescribed performance guarantee and enter into a contract agreement within the specified period if awarded the contract.
-
Contract Bond: It assures the public entity, the developer, the subcontractor, and the supplier that the contractor will fulfil its contractual obligations.
-
Customs and Court Bond: Usually, the Obligee in this type of guarantee is a government agency, such as a tax office, customs office, or court. It is used to guarantee the payment of a public receivable incurred from opening a civil case, clearing goods from customs, or incurred due to incorrect customs procedures.
-
Performance Bond: The bond gives the obligee assurance that he will be protected if the Principal or contractor fails to perform the contract
-
Retention Money: The insurance company retains the balance amount on behalf of the obligee till the contract is completed.
Insurance companies will now be able to provide sureties in the form of a cover for infrastructure companies and will become a viable alternative to bank guarantees.
Applicability
-
Under the Insurance Act of 1938, all insurers licensed to transact the general insurance business can transact the surety insurance business.
-
After the commencement of these guidelines, no entity shall transact the business of Surety Insurance in India unless the entity is an Indian Insurance Company.
-
Surety Insurance contracts shall be issued only to specific projects and not clubbed for multiple projects.
Surety insurance contracts can be offered for infrastructure projects, whether government or private.
Key Highlights
-
General Insurer must maintain the solvency rate of not below 1.25 times the control level of solvency specified by the Authority.
-
The annual premium charged for all Surety Insurance policies, including all instalments falling due in subsequent year/s for those policies, shall be restricted to 10% of that year's total gross written premium, subject to a maximum of Rs. 500 crores.
-
The guaranteed limit shall be restricted to 30% of the contract value.
-
Surety Insurance contracts shall be issued if the underlying assets/commitment are/is in India. Further, the premium and claim amount under the Surety Insurance contracts shall be in Indian rupees.
-
The insurer cannot issue a Surety Insurance contract on behalf of its promoters/subsidiaries, groups, associates and related parties.
In Conclusion
The surety would facilitate MSMEs; however, it will be more expensive than a normal bank guarantee because it is unsecured. Moreover, the industry is not yet ready to provide the cover, and it will take time to file insurance with the regulator. Sure, the new financial instrument will come with its challenges with rigorous underwriting required given the unsecured nature but definitely could be viewed as a viable alternative to BGs. Given the government's impetus in the infra sector, this might be a game-changer.
Related Articles
Categories

Insurance Detariffication: The Road Ahead
March 16, 20 | 5 min read

How tech is disrupting the insurance industry in India.
March 16, 20 | 6 min read

Insurance Industry in India & its Future
March 16, 20 | 6 min read
About the Author
More from PrishaPolicy

A necessity for one and all
March 16, 20 | 6 min read

Insurance Detariffication: The Road Ahead
March 16, 20 | 5 min read
How tech is disrupting the insurance industry in India.
March 16, 20 | 6 min read

Insurance Industry in India & its Future
March 16, 20 | 6 min read

What is motor insurance?
March 16, 23 | 6 min read

9 Reasons why your motor claim is rejected
October 16, 23 | 6 min read
